Researchers fabricate moisture-adsorbent porous graphene using a bottom-up process, with high designability and controllability of pore structures
Water purification, gas separation, and storage applications require materials with high sensitivity. Porous graphene, which possesses uniform pore structures and unique adsorption properties, is an ideal candidate for such applications. Recently, researchers from Chiba University, Japan, have developed fullerene-pillared porous graphene with high designability and controllability of pore structures using a bottom-up approach. The graphene with a 25% fullerene filling ratio is shown to exhibit the best adsorption capacity and nanopore uniformity.
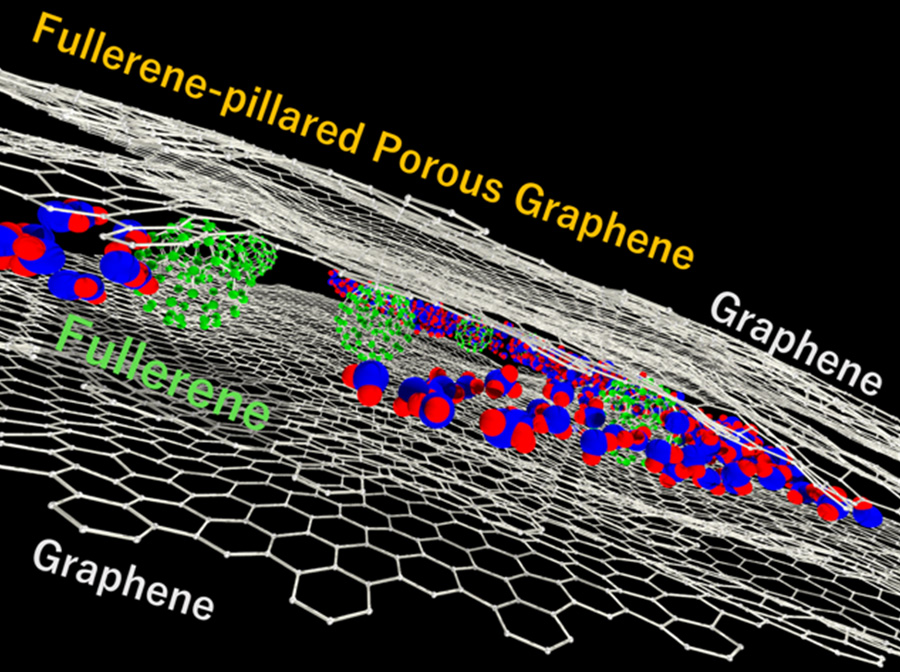
Image caption: Fullerene-pillared porous graphene with 25 ± 8% fullerene filling ratio had uniform nanopores and the largest water vapor adsorption capacity at 40% relative humidity, with potential applications in gas and liquid purification and concentration processes.
Image credit: Tomonori Ohba from Chiba University
License type: Original content
Separation processes are essential in the purification and concentration of a target molecule during water purification, removal of pollutants, and heat pumping, accounting for 10–15% of global energy consumption. To make the separation processes more energy efficient, improvement in the design of porous materials is necessary. This could drastically reduce energy costs by about 40–70%. The primary approach to improving the separation performance is to precisely control the pore structure.
In this regard, porous carbon materials offer a distinct advantage as they are composed of only one type of atom and have been well-used for separation processes. They have large pore volumes and surface areas, providing high performance in gas separation, water purification, and storage. However, pore structures generally have high heterogeneity with low designability. This poses various challenges, limiting the applicability of carbon materials in separation and storage.
Now, a team of researchers from Japan, led by Associate Professor Tomonori Ohba from Chiba University and including master’s students, Mr. Kai Haraguchi and Mr. Sogo Iwakami, has fabricated fullerene-pillared porous graphene (FPPG)—a carbon composite comprising nanocarbons—using a bottom-up approach with highly designable and controllable pore structures. They detail the synthesis, characterization, and properties of this novel water-adsorbent material in a recent article made available online on June 16, 2023, and published in Volume 127, Issue 25 of The Journal of Physical Chemistry C on June 29, 2023.
The researchers fabricated FPPG in the form of a fullerene–graphene–fullerene sandwich structure by adding a fullerene solution to graphene. They lightly coated the fullerene–graphene composition and laminated it 1–10 times. The novel tuning capability in their synthesis enabled precise control of the fullerene filling in porous graphene.
After developing FPPG structures with different fullerene filling ratios, the researchers employed experimental techniques and grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations to investigate their water vapor adsorption properties. They found that 4% fullerene-filled graphene only slightly adsorbed water vapor. Upon increasing the fullerene filling to 5%, the adsorption amount decreased further, owing to the collapse of nanopores in the laminar porous graphene. However, increasing the filling ratio close to 25% yielded a surprising outcome. “FPPG with 25 ± 8% fullerene had the largest water vapor adsorption capacity at 40% relative humidity owing to the production of large uniform nanopores,” highlights Dr. Ohba.
Further increasing the fullerene filling ratio in FPPG, up to 50% fullerene, diminished the adsorption capabilities. The Monte Carlo simulations agreed with these observations, revealing that the excess fullerene content reduced the nanopores, which, in turn, prevented water cluster formation.
“The bottom-up technique, along with designable and controllable pore structures of FPPG, can facilitate the development of more such novel materials that would considerably improve the performance of gas and liquid purification and concentration processes,” speculates an optimistic Dr. Ohba. “This, in turn, would considerably bring down the costs of numerous products manufactured via separation processes.”
Together, novel porous carbons such as FPPG could potentially revolutionize storage and purification applications, making them more energy efficient and cost-effective.
About Associate Professor Tomonori Ohba
Tomonori Ohba is an Associate Professor and director of the Ohba Research Group at the Department of Chemistry at the Graduate School of Science at Chiba University in Japan. He primarily works in the field of physical chemistry, with a research goal to elucidate chemical phenomena at the nanomolecular levels by employing theoretical as well as experimental methods. He also explores nanospaces to control molecular motion, investigate molecular behavior, and discover new molecular reactivities. His extensive research work, published in numerous reputed journals, has been cited more than 5,000 times.
Reference
Title of original paper: Fabrication of Fullerene-Pillared Porous Graphene and Its Water Vapor Adsorption
Authors: Kai Haraguchi, Sogo Iwakami, and Tomonori Ohba
Affiliation: Graduate School of Science, Chiba University, Japan
Journal: The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c02394
Contact
Tomonori OHBA
Graduate School of Science, Chiba University, Japan
Address: 1-33 Yayoi, Inage, Chiba 263-8522 JAPAN
Email: ohba@chiba-u.jp
Public Relations Office, Chiba University
Address: 1-33 Yayoi, Inage, Chiba 263-8522, JAPAN
Email: koho-press@chiba-u.jp


-200x150.jpg)

