A new design involving a foldable pouch actuator developed by Chiba University researchers holds promise in clinical hand rehabilitation applications
Hand rehabilitation research has markedly benefitted from the introduction of soft actuators in gloves. However, existing soft rehabilitation glove designs have several limitations in finger movements. In this regard, Chiba University researchers recently succeeded in adding finger straightening or extension to soft rehabilitation gloves through a novel foldable pouch actuator without compromising the already existing functionality of finger bending or flexion. Their findings represent a significant leap in comprehensive hand rehabilitation.
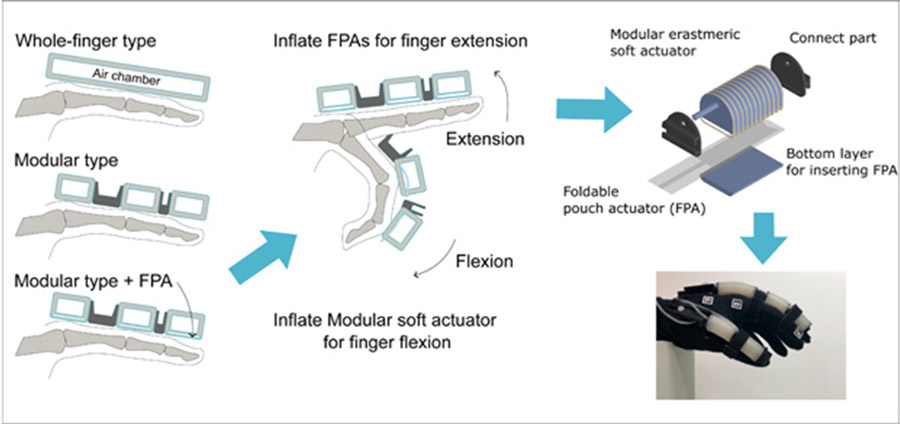
Image title: Novel foldable pouch actuators improve soft rehabilitation glove design
Image caption: Chiba University researchers succeeded in overcoming limitations associated with finger straightening or extension without compromising existing functionality of finger bending or flexion through design improvements in soft rehabilitation gloves—they developed a novel foldable pouch actuator that seamlessly integrates with existing soft actuators used in the gloves.
Image credit: Professor Wenwei Yu from Chiba University, Japan
Image license: CC BY 4.0
Soft rehabilitation gloves have become popular tools for helping patients with hand function-related disabilities recover finger movement. These gloves often use soft pneumatic actuators that employ air pressure to generate movements. Despite significant design improvements in recent years, many available soft actuators have drawbacks in achieving bidirectional motion typical of finger joints—such soft actuators facilitate finger bending (or flexion) but not finger straightening (or extension).
A group of biomedical researchers from Chiba University successfully overcame this design limitation by developing a novel foldable pouch actuator (FPA) that seamlessly integrated with existing soft actuators in the rehabilitation gloves. Professor Wenwei Yu from the Center for Frontier Medical Engineering, Chiba University, Japan, led the research group that accomplished this feat. The research group also included Dr. Shota Kokubu and Mr. Pablo E. Tortós Vinocour from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University, Japan. They published their findings in IEEE Access on 30 April 2024.
When asked about the motivation for the study, Prof. Yu explains, “Despite having partial hand function, many older people with hand function-related disabilities whom I’ve come across require the full attention of the healthcare staff. I wondered if an efficient and safe assistive device could bolster their hand function for daily activities, thus helping them enjoy their life better. Imagine their joy in eating their meals using their hands to manipulate spoons or chopsticks!” The FPA has indeed brought the world one step closer to this reality.
The FPA is the first-ever joint-modular bi-directional soft actuator, thanks to the efforts of Prof. Yu and his research group. It comprises a single sheet flat, foldable structure that expands only when it is pressurized, thus generating the requisite force for finger extension.
Notably, the FPA facilitates finger extension in the soft rehabilitation gloves without compromising the existing functionality offered by the other soft actuators, such as finger flexion realized by fiber-reinforced elastomer-based actuators. They confirmed their findings through tests on a synthetic finger model. Results from the model showed that the integrated soft actuator could produce sufficient torque (force) for the required finger movements, including a joint bending torque of 0.17 Newton meters (Nm) and an estimated straightening torque of 0.12 Nm.
The improved design of the soft rehabilitation glove could have far-reaching clinical applications. Prof. Yu mentions a few potential applications of the upgraded soft rehabilitation gloves, all thanks to the inclusion of the FPA, “High-performance modular soft actuators could help hand function restoration in both telerehabilitation and care facility scenarios.” He adds, “The new soft actuator has the potential to be used not only for helping rehabilitation but also for assisting daily living activity as assistive devices. Due to its inherent safety, high functionality, and wearability, such assistive devices may play a major role in our aging society.”
Prof. Yu also suggested that future soft rehabilitation glove designs could benefit from enhancing manufacturing precision and controlling systems for supporting joint-specific rehabilitation.
In conclusion, Prof. Yu and his research group have succeeded in offering hope to many patients experiencing hand function-related disabilities worldwide, all thanks to the FPA and, by extension, improved soft rehabilitation gloves.
About Professor Wenwei Yu
Dr. Wenwei Yu has been a professor (since 2009) and the vice director (since 2013) at the Center for Frontier Medical Engineering, Chiba University, Japan. Prof. Yu heads the Yu Laboratory, which houses research groups primarily in electrophysiological stimulation, human behavior monitoring, and soft robotics. He leads cutting-edge biomedical research in rehabilitation robotics, care support technology, and portable low-field magnetic resonance imaging. His credentials include authoring and co-authoring over 175 research papers in reputed publications and leading more than 15 multidisciplinary research projects.
Funding:
This work was partly supported by the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI under Grant JP23KJ0307.
Reference:
Title of original paper: Bidirectional Support for Individual Finger Joints in Soft Rehabilitation Gloves: Integration of Foldable Pouch Actuators with Modular Elastomeric Actuators
Authors: Shota Kokubu1, Pablo E. Tortós Vinocour1, and Wenwei Yu1,2
Affiliations:
1Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University, Japan
2Center for Frontier Medical Engineering, Chiba University, Japan
Journal: IEEE Access
DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3395468
Contact: Wenwei Yu
Center for Frontier Medical Engineering, Chiba University
Email: yuwill@faculty.chiba-u.jp
Public Relations Office, Chiba University
Address: 1-33 Yayoi, Inage, Chiba 263-8522 JAPAN
Email: koho-press@chiba-u.jp
Tel: +81-43-290-2018





